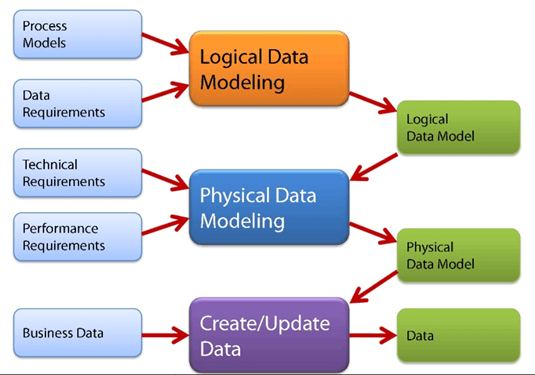
What is Data Modelling?
Data modeling is the process of creating a data model for the data to be stored in a Database. This data model is a conceptual representation of
- Data objects
- The associations between different data objects
- The rules.
Data modeling helps in the visual representation of data and enforces business rules, regulatory compliances, and government policies on the data. Data Models ensure consistency in naming conventions, default values, semantics, security while ensuring quality of the data.
Data model emphasizes on what data is needed and how it should be organized instead of what operations need to be performed on the data. Data Model is like architect’s building plan which helps to build a conceptual model and set the relationship between data items.
The two types of Data Models techniques are
- Entity Relationship (E-R) Model
- UML (Unified Modelling Language)
Why use Data Model?
The primary goal of using data model are:
- Ensures that all data objects required by the database are accurately represented. Omission of data will lead to creation of faulty reports and produce incorrect results.
- A data model helps design the database at the conceptual, physical and logical levels.
- Data Model structure helps to define the relational tables, primary and foreign keys and stored procedures.
- It provides a clear picture of the base data and can be used by database developers to create a physical database.
- It is also helpful to identify missing and redundant data.
- Though the initial creation of data model is labor and time consuming, in the long run, it makes your IT infrastructure upgrade and maintenance cheaper and faster.
Types of Data Models
There are mainly three different types of data models:
- Conceptual: This Data Model defines WHAT the system contains. This model is typically created by Business stakeholders and Data Architects. The purpose is to organize, scope and define business concepts and rules.
- Logical: Defines HOW the system should be implemented regardless of the DBMS. This model is typically created by Data Architects and Business Analysts. The purpose is to developed technical map of rules and data structures.
- Physical: This Data Model describes HOW the system will be implemented using a specific DBMS system. This model is typically created by DBA and developers. The purpose is actual implementation of the database.
Conceptual Model
The main aim of this model is to establish the entities, their attributes, and their relationships. In this Data modeling level, there is hardly any detail available of the actual Database structure.
The 3 basic tenants of Data Model are
Entity: A real-world thing
Attribute: Characteristics or properties of an entity
Relationship: Dependency or association between two entities
For example:
- Customer and Product are two entities. Customer number and name are attributes of the Customer entity
- Product name and price are attributes of product entity
- Sale is the relationship between the customer and product
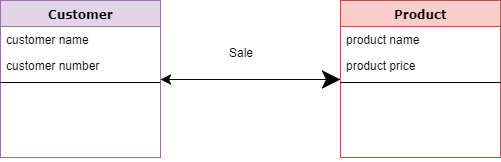
Characteristics of a conceptual data model
- Offers Organisation-wide coverage of the business concepts.
- This type of Data Models are designed and developed for a business audience.
- The conceptual model is developed independently of hardware specifications like data storage capacity, location or software specifications like DBMS vendor and technology. The focus is to represent data as a user will see it in the “real world.”
Conceptual data models known as Domain models create a common vocabulary for all stakeholders by establishing basic concepts and scope.
Logical Data Model
Logical data models add further information to the conceptual model elements. It defines the structure of the data elements and set the relationships between them.
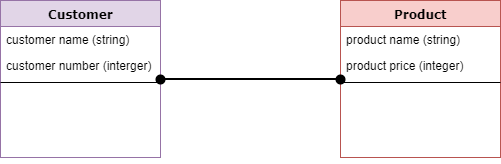
The advantage of the Logical data model is to provide a foundation to form the base for the Physical model. However, the modeling structure remains generic.
At this Data Modeling level, no primary or secondary key is defined. At this Data modeling level, you need to verify and adjust the connector details that were set earlier for relationships.
Characteristics of a Logical data model
- Describes data needs for a single project but could integrate with other logical data models based on the scope of the project.
- Designed and developed independently from the DBMS.
- Data attributes will have datatypes with exact precisions and length.
- Normalization processes to the model is applied typically till 3NF.
Physical Data Model
A Physical Data Model describes the database specific implementation of the data model. It offers an abstraction of the database and helps generate schema. This is because of the richness of meta-data offered by a Physical Data Model.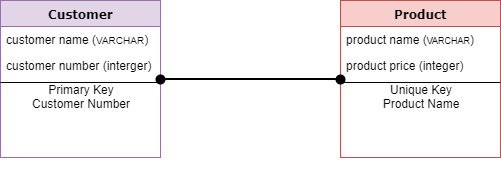
This type of Data model also helps to visualize database structure. It helps to model database columns keys, constraints, indexes, triggers, and other RDBMS features.
Characteristics of a physical data model:
- The physical data model describes data need for a single project or application though it maybe integrated with other physical data models based on project scope.
- Data Model contains relationships between tables that which addresses cardinality and nullability of the relationships.
- Developed for a specific version of a DBMS, location, data storage or technology to be used in the project.
- Columns should have exact datatypes, lengths assigned and default values.
- Primary and Foreign keys, views, indexes, access profiles, and authorizations, etc. are defined.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Model:
Advantages of Data model:
- The main goal of a designing data model is to make certain that data objects offered by the functional team are represented accurately.
- The data model should be detailed enough to be used for building the physical database.
- The information in the data model can be used for defining the relationship between tables, primary and foreign keys, and stored procedures.
- Data Model helps business to communicate the within and across organizations.
- Data model helps to documents data mappings in ETL process
- Help to recognize correct sources of data to populate the model
Disadvantages of Data model:
- To develop Data model one should know physical data stored characteristics.
- This is a navigational system produces complex application development, management. Thus, it requires a knowledge of the biographical truth.
- Even smaller change made in structure require modification in the entire application.
- There is no set data manipulation language in DBMS.
Conclusion
- Data modeling is the process of developing data model for the data to be stored in a Database.
- Data Models ensure consistency in naming conventions, default values, semantics, security while ensuring quality of the data.
- Data Model structure helps to define the relational tables, primary and foreign keys and stored procedures.
- There are three types of conceptual, logical, and physical.
- The main aim of conceptual model is to establish the entities, their attributes, and their relationships.
- Logical data model defines the structure of the data elements and set the relationships between them.
- A Physical Data Model describes the database specific implementation of the data model.
- The main goal of a designing data model is to make certain that data objects offered by the functional team are represented accurately.
- The biggest drawback is that even smaller change made in structure require modification in the entire application.